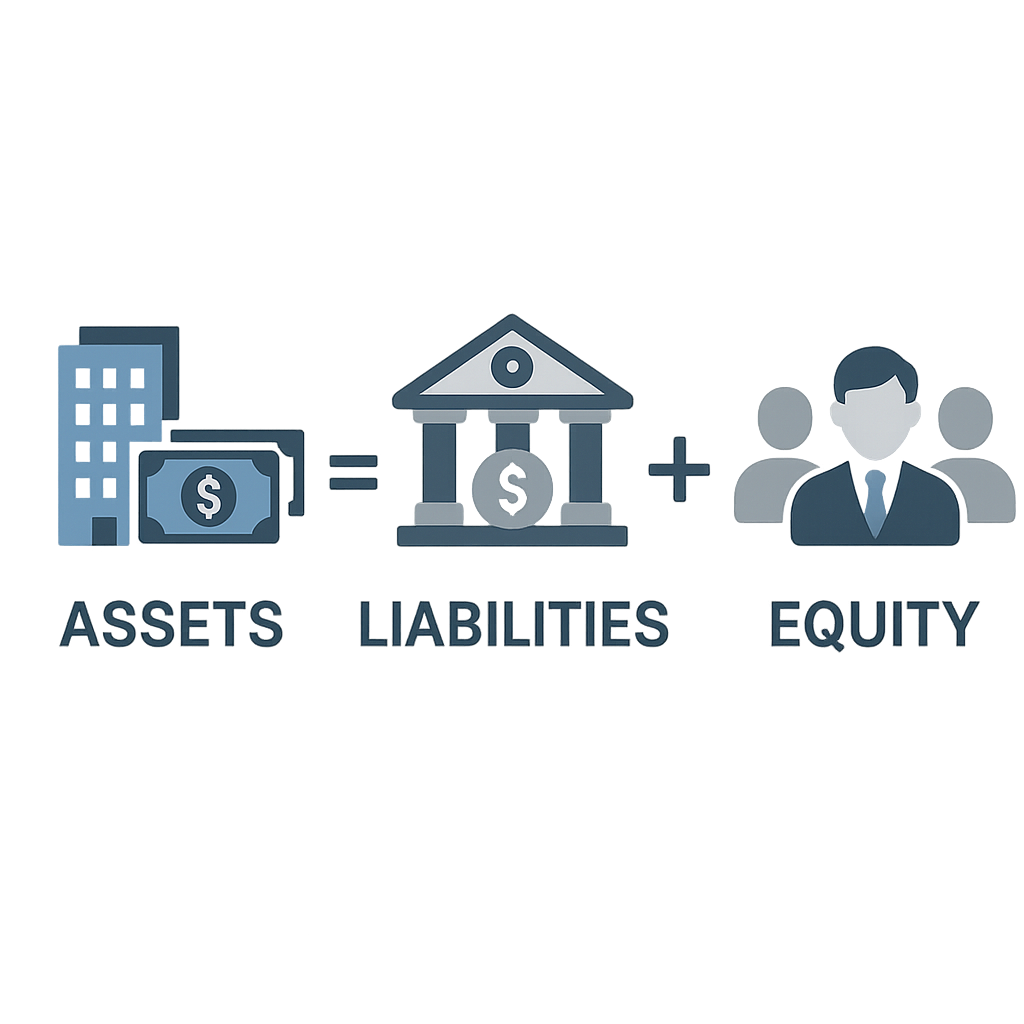
Most business owners struggle with understanding their company’s financial health, often making costly decisions based on incomplete information. The accounting equation holds the key to unlocking your business’s true financial position, but there are three critical secrets that separate successful entrepreneurs from those who fail. Master these fundamentals and transform how you manage your business finances forever.
Secret #1:
The Hidden Power of the Basic Accounting Equation
The accounting equation is more than just a mathematical formula—it’s your business’s financial DNA. This fundamental principle ensures that every transaction in your business maintains perfect balance, providing the foundation for all financial decision-making.
The Basic Formula That Rules Everything

Assets = Liabilities + Equity
This simple equation can also be expressed as:
- Equity = Assets – Liabilities
- Liabilities = Assets – Equity
Here’s why this matters: If your numbers don’t balance, it signals errors in your financial records that could lead to poor business decisions, tax problems, or cash flow disasters.
Breaking Down the Three Components
Assets: Everything Your Business Owns or Controls
Assets represent all valuable resources your business possesses. Understanding the distinction between current and non-current assets is crucial for cash flow management:
Current Assets (convertible to cash within one year):
- Cash and cash equivalents
- Accounts receivable (customer payments due)
- Inventory ready for sale
- Prepaid expenses (insurance, rent paid in advance)
- Short-term investments
Non-Current Assets (long-term value creators):
- Property, buildings, and real estate
- Equipment, vehicles, and machinery
- Patents, trademarks, and intellectual property
- Goodwill and brand value
- Long-term investments
Liabilities: Every Dollar Your Business Owes
Liabilities are financial obligations that represent claims against your assets. Managing these effectively determines your business’s financial stability:
Current Liabilities (due within one year):
- Accounts payable (supplier bills)
- Short-term loans and credit lines
- Accrued expenses (unpaid wages, utilities)
- Taxes owed to government agencies
- Customer deposits and deferred revenue
Long-Term Liabilities (due after one year):
- Mortgages and long-term loans
- Equipment financing agreements
- Pension and retirement obligations
- Long-term lease commitments
Equity: Your True Ownership Stake
Equity represents what’s left after paying all debts—essentially your ownership value in the business:
For Sole Proprietorships and Partnerships:
- Owner’s initial capital investment
- Additional contributions over time
- Retained earnings (accumulated profits)
- Owner withdrawals (money taken out)
For Corporations:
- Common stock issued to shareholders
- Preferred stock and special shares
- Retained earnings from operations
- Additional paid-in capital
Secret #2: My Favorite
The Expanded Accounting Equation Reveals Hidden Financial Truths
While most business owners stop at the basic equation, successful entrepreneurs understand the expanded accounting equation that breaks down equity into its operating components, revealing how daily business activities affect financial position.
The Game-Changing Expanded Formula
While most business owners stop at the basic equation, successful entrepreneurs understand the expanded accounting equation that breaks down equity into its operating components, revealing how daily business activities affect financial position.
Assets = Liabilities + Owner’s Capital + (Revenues – Expenses – Withdrawals)
For corporations, this becomes:
Assets = Liabilities + Paid-in Capital + (Revenues – Expenses – Dividends)
Why the Expanded Equation is Critical
This expanded version shows how your income statement activities (revenues and expenses) directly impact your balance sheet equity. When you close your books each period, net income flows into retained earnings, permanently changing your equity structure.
The Alternative Form for Double-Entry Mastery:
Assets + Expenses = Liabilities + Equity + Revenues
This arrangement reveals the “golden rules” of double-entry bookkeeping:
- Left side (Debits): Assets and Expenses increase with debits
- Right side (Credits): Liabilities, Equity, and Revenues increase with credits
Practical Application Example
Consider Sarah’s consulting business with these numbers:
- Assets: $150,000 (cash, equipment, receivables)
- Liabilities: $50,000 (loans, payables)
- Owner’s Capital: $80,000 (initial investment)
- Revenues: $60,000 (consulting fees earned)
- Expenses: $30,000 (rent, salaries, supplies)
- Owner Withdrawals: $10,000 (personal draws)
Expanded Equation Verification:
$150,000 = $50,000 + $80,000 + ($60,000 – $30,000 – $10,000)
$150,000 = $50,000 + $80,000 + $20,000
$150,000 = $150,000 ✓
This shows Sarah’s business added $20,000 to equity through profitable operations.
Secret #3:
How Every Transaction Maintains Perfect Balance
The most powerful secret is understanding how every business transaction affects the equation while maintaining balance. This knowledge transforms you from a passive observer to an active financial manager.
Real-World Transaction Examples
Example 1: Starting with Capital
Sarah invests $25,000 cash to start her business:
- Assets increase: +$25,000 (cash)
- Equity increases: +$25,000 (owner’s capital)
- Balance check: $25,000 = $0 + $25,000 ✓
Example 2: Securing Business Financing
Sarah obtains a $15,000 bank loan:
- Assets increase: +$15,000 (cash)
- Liabilities increase: +$15,000 (bank loan)
- New totals: $40,000 = $15,000 + $25,000 ✓
Example 3: Purchasing Equipment
Sarah buys $8,000 worth of office equipment with cash:
- Assets shift: -$8,000 cash, +$8,000 equipment
- Net asset change: $0
- Balance maintained: $40,000 = $15,000 + $25,000 ✓
Example 4: Earning Revenue
Sarah completes a $5,000 consulting project:
- Assets increase: +$5,000 (cash or receivables)
- Equity increases: +$5,000 (retained earnings)
- New balance: $45,000 = $15,000 + $30,000 ✓
Example 5: Operating Expenses
Sarah pays $2,000 in monthly operating expenses:
- Assets decrease: -$2,000 (cash)
- Equity decreases: -$2,000 (retained earnings)
- Updated balance: $43,000 = $15,000 + $28,000 ✓
The Double-Entry Connection
Every transaction follows the double-entry principle:
- Each transaction affects at least two accounts
- Total debits must equal total credits
- The accounting equation always stays balanced
This system provides built-in error checking and ensures accurate financial reporting.
Advanced Strategies for Business Success
Using the Equation for Financial Analysis
Debt-to-Equity Ratio Calculation:
Total Liabilities ÷ Total Equity = Financial Leverage
- High ratios: Indicate dependency on debt financing
- Low ratios: Suggest strong financial independence
- Industry benchmarks: Compare against competitors
Return on Equity (ROE) Assessment:
Net Income ÷ Average Equity = Profitability Efficiency
This measures how effectively your business generates profits from owner investments.
Cash Flow Planning Applications
Understanding asset composition helps predict cash needs:
- Current Ratio: Current Assets ÷ Current Liabilities
- Quick Ratio: (Current Assets – Inventory) ÷ Current Liabilities
- Working Capital: Current Assets – Current Liabilities
Investment Decision Framework
The equation guides major business decisions:
- Equipment purchases: How will assets and financing change?
- Expansion plans: What’s the impact on debt-to-equity ratios?
- Dividend payments: How do distributions affect retained earnings?
Common Mistakes That Cost Businesses Money
Mistake #1: Confusing Assets with Expenses
Problem: Recording equipment purchases as immediate expenses
Solution: Capitalize assets that provide future benefits beyond one year
Mistake #2: Ignoring Owner Transactions
Problem: Not tracking owner contributions and withdrawals properly
Solution: Maintain separate capital accounts for all owner transactions
Mistake #3: Poor Liability Classification
Problem: Misclassifying short-term vs. long-term obligations
Solution: Review payment terms and categorize based on due dates
Mistake #4: Neglecting Accrual Accounting
Problem: Only recording transactions when cash changes hands
Solution: Record revenues when earned and expenses when incurred
Technology Solutions for Modern Businesses
Cloud-Based Accounting Software Benefits
Modern platforms automatically maintain equation balance through:
- Real-time transaction recording with built-in error checking
- Automated bank reconciliation reducing manual errors
- Integrated financial reporting showing live balance sheets
- Multi-user access with appropriate permission controls
Essential Features to Look For
- Automatic equation balancing with error alerts
- Customizable chart of accounts for your industry
- Real-time financial dashboards showing key ratios
- Audit trails for all transactions and changes
Industry-Specific Applications
Service-Based Businesses
- Lower asset requirements with focus on current assets
- Emphasis on accounts receivable management
- Higher profit margins improving equity growth
Manufacturing Companies
- Significant fixed asset investments in equipment
- Complex inventory valuation affecting current assets
- Higher leverage ratios from equipment financing
Retail Operations
- Inventory-heavy asset structures requiring careful management
- Seasonal fluctuations in working capital needs
- Credit line management for inventory purchases
Future-Proofing Your Financial Understanding
Digital Asset Considerations
Modern businesses must account for:
- Cryptocurrency holdings as current or long-term assets
- Software licenses and subscription assets
- Intellectual property and digital content
- Customer databases and data assets
Sustainability Accounting
Emerging requirements include:
- Environmental cleanup liabilities for manufacturing
- Carbon credit assets and environmental obligations
- ESG investment tracking in asset portfolios
- Social responsibility provisions in liability accounts
Taking Action: Your Next Steps
Immediate Implementation Plan
- Set up proper bookkeeping: Use accounting software that enforces equation balance
- Create monthly balance sheets: Review your financial position regularly
- Calculate key ratios: Monitor debt-to-equity and return on equity monthly
- Separate business and personal: Maintain clear boundaries for owner transactions
Monthly Financial Review Process
- Verify equation balance: Ensure Assets = Liabilities + Equity
- Analyze ratio trends: Track changes in financial leverage
- Review cash flow: Monitor current ratio and working capital
- Plan for growth: Assess financing needs for expansion
Professional Support Strategy
- Quarterly accountant reviews: Ensure accuracy and compliance
- Annual financial audits: For larger businesses requiring investor confidence
- Tax planning sessions: Optimize timing of income and expenses
- Business advisory meetings: Strategic planning based on financial position
The Bottom Line
The accounting equation isn’t just an academic concept—it’s your financial compass for business success. By mastering these three critical secrets, you gain the power to:
- Make informed decisions based on complete financial pictures
- Identify problems early before they become crises
- Plan for sustainable growth with proper financial foundations
- Communicate effectively with lenders, investors, and partners
Whether you’re launching a startup or managing an established business, these principles provide the clarity needed to build lasting financial success. The equation’s balance reflects your business’s balance—master one to achieve the other.
Start implementing these strategies today, and watch your financial confidence grow along with your business prosperity. Remember: every successful business owner understands their numbers, and it all begins with the fundamental accounting equation that governs everything.
Ready to transform your business finances? Begin by creating a simple balance sheet using the accounting equation, then review it monthly to track your progress and spot opportunities for improvement. Your future self will thank you for taking control of your financial destiny today.